| Secciones |
|---|
| Foros Electrónica |
|
|
| Boletines de correo |
 |
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 1
93C76/86
Features:
Single 5.0V supply
Low-power CMOS technology
- 1 mA active current typical
ORG pin selectable memory configuration
1024 x 8- or 512 x 16-bit organization (93C76)
2048 x 8- or 1024 x 16-bit organization (93C86)
Self-timed erase and write cycles
(including auto-erase)
Automatic ERAL before WRAL
Power on/off data protection circuitry
Industry standard 3-wire serial I/O
Device status signal during erase/write cycles
Sequential read function
1,000,000 erase/write cycles ensured
Data retention > 200 years
8-pin PDIP/SOIC package
Temperature ranges supported
Description:
The Microchip Technology Inc. 93C76/86 are 8K and
16K low voltage serial Electrically Erasable PROMs.
The device memory is configured as x8 or x16 bits
depending on the ORG pin setup. Advanced CMOS
technology makes these devices ideal for low power
nonvolatile memory applications. These devices also
have a Program Enable (PE) pin to allow the user to
write protect the entire contents of the memory array.
The 93C76/86 is available in standard 8-pin PDIP and
8-pin surface mount SOIC packages.
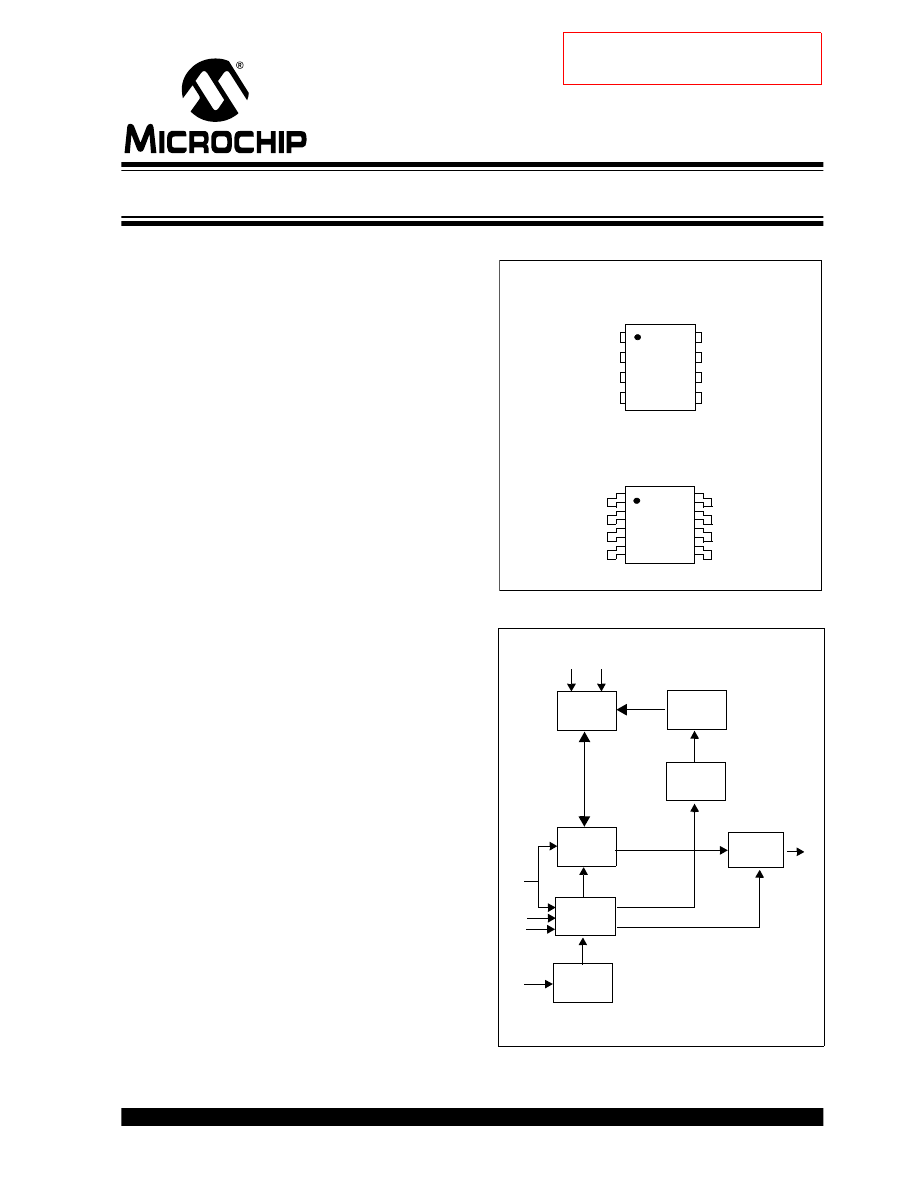
Package Types
Block Diagram
- Commercial (C):
0 °C
to
+70 °C
- Industrial (I):
-40 °C to
+85 °C
- Automotive (E)
-40 °C to +125 °C
SOIC Package
PDIP Package
CS
CLK
DI
DO
V
SS
PE
V
CC
ORG
CS
CLK
DI
DO
V
CC
PE
ORG
V
SS
93
C
7
6/
8
6
93
C
7
6/8
6
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
DO
CS
CLK
V
CC
V
SS
Memory
Array
Address
Decoder
Data
Register
Counter
Address
Output
Buffer
Mode
Decode
Logic
Generator
Clock
DI
PE
8K/16K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM
Not recommended for new designs -
Please use 93LC76C or 93LC86C.
93C76/86
DS21132F-page 2
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
( )
V
CC
.............................................................................................................................................................................7.0V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
SS
........................................................................................................ -0.6V to Vcc + 1.0V
Storage temperature ...............................................................................................................................-65 °C to +150 °C
Ambient temperature with power applied ................................................................................................-40 °C to +125 °C
Soldering temperature of leads (10 seconds) ....................................................................................................... +300 °C
ESD protection on all pins .......................................................................................................................................... 4 kV
1.1
AC Test Conditions
NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
AC Waveform:
V
LO
= 2.0V
V
HI
= Vcc - 0.2V
)
V
HI
= 4.0V for
)
Timing Measurement Reference Level
Input
0.5 V
CC
Output
0.5 V
CC
Note 1:
For V
CC
ï£ 4.0V
2:
For V
CC
> 4.0V
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 3
93C76/86
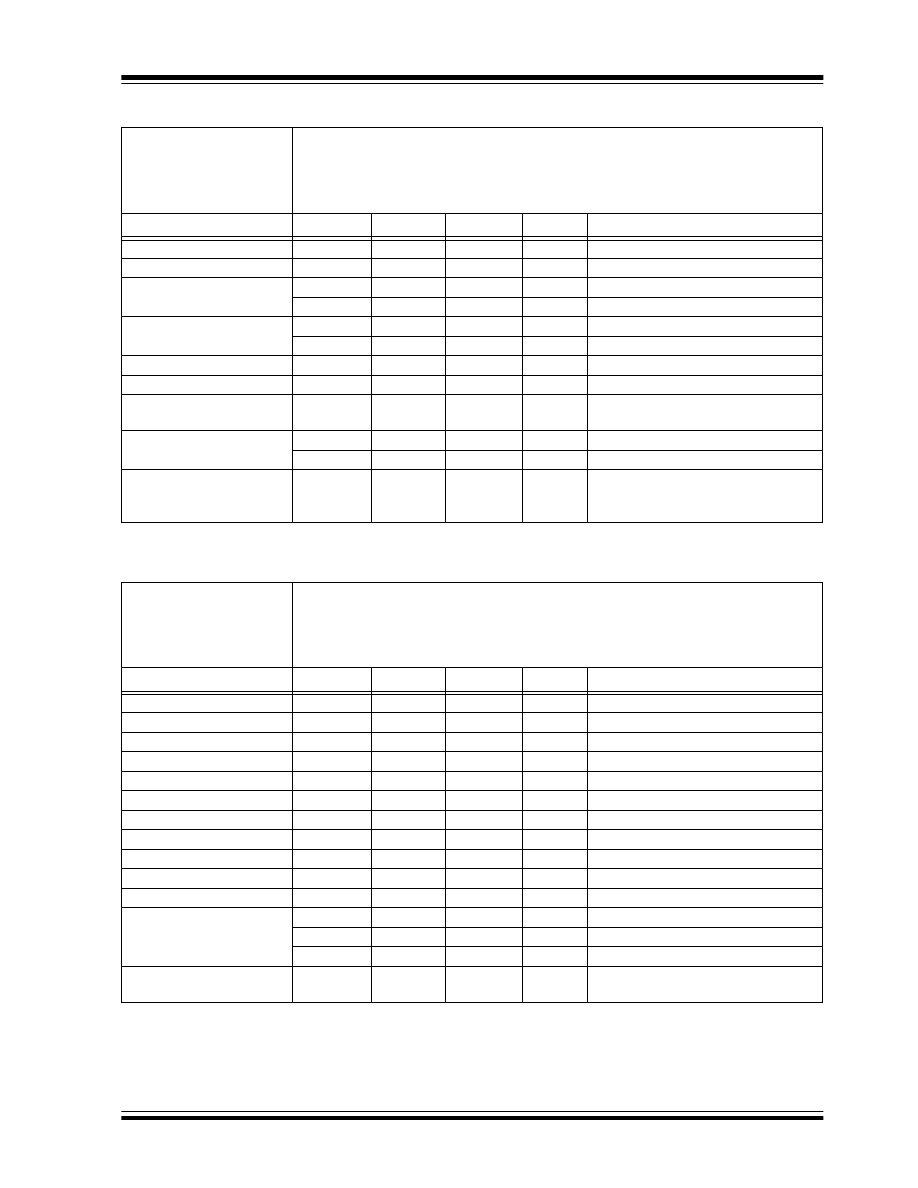
TABLE 1-1:
DC CHARACTERISTICS
TABLE 1-2:
AC CHARACTERISTICS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Applicable over recommended operating ranges shown below unless otherwise noted:
V
CC
= +4.5V to +5.5V
Commercial (C): T
A
= 0 °C to -40 °C
Industrial (I):
T
A
= -40 °C to +85 °C
Automotive (E): T
A
= -40
ï°C to +125ï°C
Parameter
Symbol
Min.
Max.
Units
Conditions
High-level input voltage
V
IH1
2.0
V
CC
+1
V
Low-level input voltage
V
IL1
-0.3
0.8
V
Low-level output voltage
V
OL1
0.4
V
I
OL
= 2.1 mA; V
CC
= 4.5V
V
OL2
0.2
V
I
OL
=100
µA; V
CC
= 4.5V
High-level output voltage
V
OH1
2.4
V
I
OH
= -400
µA; V
CC
= 4.5V
V
OH2
V
CC
-0.2
V
I
OH
= -100
µA; V
CC
= 4.5V.
Input leakage current
I
LI
-10
10
µA
V
IN
= 0.1V to V
CC
Output leakage current
I
LO
-10
10
µA
V
OUT
= 0.1V to V
CC
Pin capacitance
(all inputs/outputs)
C
INT
7
pF
(Note 1)
T
A
= +25 °C, F
CLK
= 1 MHz
Operating current
I
CC
write
3
mA
F
CLK
= 2 MHz; V
CC
= 5.5V
I
CC
read
1.5
mA
F
CLK
= 2 MHz; V
CC
= 5.5V
Standby current
I
CCS
100
µA
CLK = CS = 0V; V
CC
= 5.5V
DI = PE = V
SS
ORG = V
SS
or V
CC
Note 1:
This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Applicable over recommended operating ranges shown below unless otherwise noted:
V
CC
= +4.5V to +5.5V
Commercial (C): T
A
= 0 °C to -40 °C
Industrial (I):
T
A
= -40 °C to +85 °C
Automotive (E): T
A
= -40
ï°C to +125ï°C
Parameter
Symbol
Min.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Clock frequency
F
CLK
2
MHz
Vcc
ï³ 4.5V
Clock high time
T
CKH
300
ns
Clock low time
T
CKL
200
ns
Chip select setup time
T
CSS
50
ns
Relative to CLK
Chip select hold time
T
CSH
0
ns
Chip select low time
T
CSL
250
ns
Relative to CLK
Data input setup time
T
DIS
100
ns
Relative to CLK
Data input hold time
T
DIH
100
ns
Relative to CLK
Data output delay time
T
PD
400
ns
C
L
= 100 pF
Data output disable time
T
CZ
100
ns
Status valid time
T
SV
500
ns
C
L
= 100 pF
Program cycle time
T
WC
10
ms
Erase/Write mode
T
EC
15
ms
ERAL mode
T
WL
30
ms
WRAL mode
Endurance
1M
cycles
25 °C, V
CC
= 5.0V, Block mode
Note 1:
This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
2:
Typical program cycle is 4 ms per word.
3:
This parameter is not tested but ensured by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific
application, please consult the Total Endurance
™
Model which can be obtained from Microchips web site
at www.microchip.com.
93C76/86
DS21132F-page 4
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
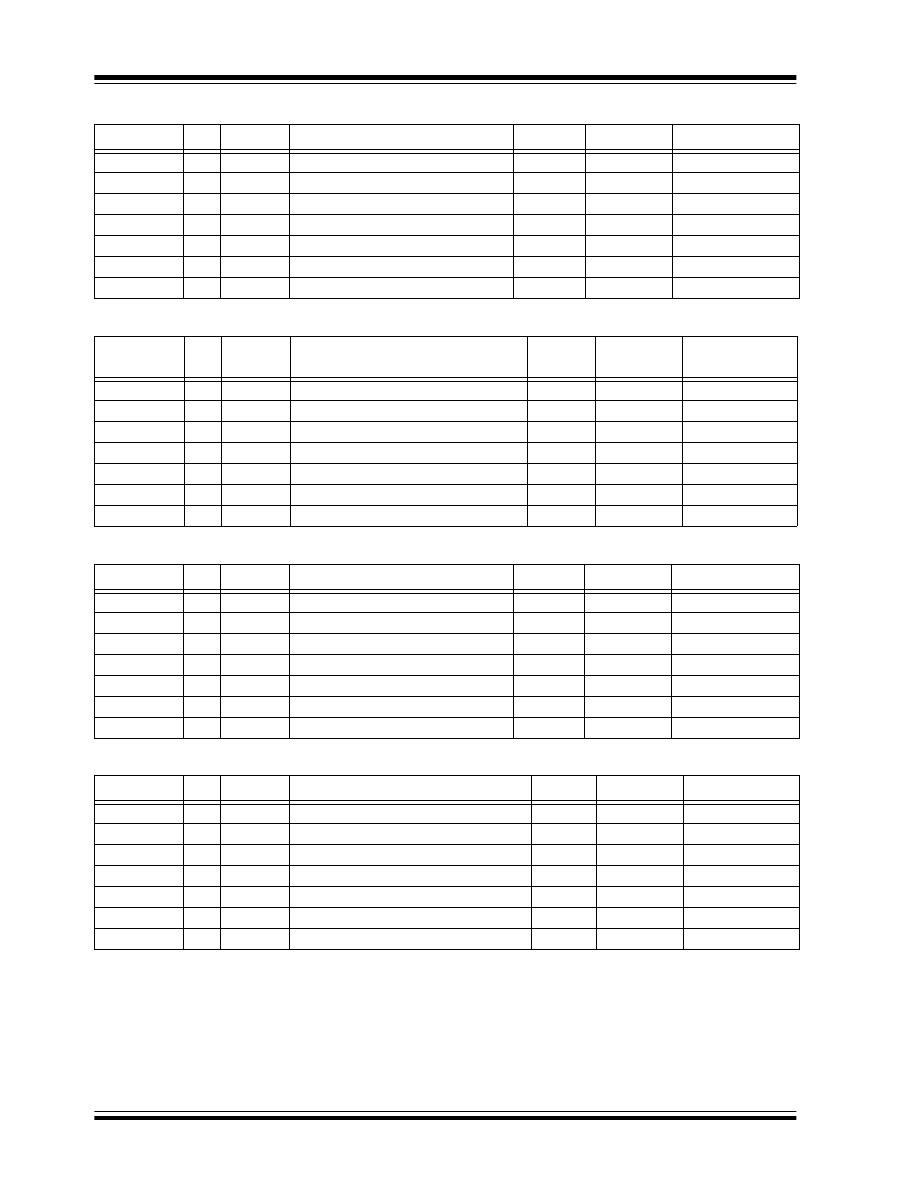
TABLE 1-3:
INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93C76: ORG=1 (X16 ORGANIZATION)
TABLE 1-4:
INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93C76: ORG=0 (X8 ORGANIZATION)
TABLE 1-5:
INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93C86: ORG=1 (X16 ORGANIZATION)
TABLE 1-6:
INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93C86: ORG=0 (X8 ORGANIZATION)
Instruction
SB
Opcode
Address
Data In
Data Out
Req. CLK Cycles
READ
1
10
X A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D15 - D0
29
EWEN
1
00
1 1 X X X X X X X X
High-Z
13
ERASE
1
11
X A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
(RDY/BSY)
13
ERAL
1
00
1 0 X X X X X X X X
(RDY/BSY)
13
WRITE
1
01
X A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D15 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
29
WRAL
1
00
0 1 X X X X X X X X
D15 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
29
EWDS
1
00
0 0 X X X X X X X X
High-Z
13
Instruction
SB
Opcode
Address
Data In
Data Out
Req. CLK
Cycles
READ
1
10
X A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 - D0
22
EWEN
1
00
1 1 X X X X X X X X X
High-Z
14
ERASE
1
11
X A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
(RDY/BSY)
14
ERAL
1
00
1 0 X X X X X X X X X
(RDY/BSY)
14
WRITE
1
01
X A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
22
WRAL
1
00
0 1 X X X X X X X X X
D7 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
22
EWDS
1
00
0 0 X X X X X X X X X
High-Z
14
Instruction
SB
Opcode
Address
Data In
Data Out
Req. CLK Cycles
READ
1
10
A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D15 - D0
29
EWEN
1
00
1 1 X X X X X X X X
High-Z
13
ERASE
1
11
A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
(RDY/BSY)
13
ERAL
1
00
1 0 X X X X X X X X
(RDY/BSY)
13
WRITE
1
01
A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D15 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
29
WRAL
1
00
0 1 X X X X X X X X
D15 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
29
EWDS
1
00
0 0 X X X X X X X X
High-Z
13
Instruction
SB
Opcode
Address
Data In
Data Out
Req. CLK Cycles
READ
1
10
A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 - D0
22
EWEN
1
00
1 1 X X X X X X X X X
High-Z
14
ERASE
1
11
A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
(RDY/BSY)
14
ERAL
1
00
1 0 X X X X X X X X X
(RDY/BSY)
14
WRITE
1
01
A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
22
WRAL
1
00
0 1 X X X X X X X X X
D7 - D0
(RDY/BSY)
22
EWDS
1
00
0 0 X X X X X X X X X
High-Z
14

ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 5
93C76/86
2.0
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
When the ORG pin is connected to V
CC
, the x16 orga-
nization is selected. When it is connected to ground,
the x8 organization is selected. Instructions, addresses
and write data are clocked into the DI pin on the rising
edge of the clock (CLK). The DO pin is normally held in
a high-Z state except when reading data from the
device, or when checking the Ready/Busy status
during a programming operation. The Ready/Busy
status can be verified during an erase/write operation
by polling the DO pin; DO low indicates that program-
ming is still in progress, while DO high indicates the
device is ready. The DO will enter the high-impedance
state on the falling edge of the CS.
2.1
Start Condition
The Start bit is detected by the device if CS and DI are
both high with respect to the positive edge of CLK for
the first time.
Before a Start condition is detected, CS, CLK and DI
may change in any combination (except to that of a
Start condition), without resulting in any device opera-
tion (Read, Write, Erase, EWEN, EWDS, ERAL and
WRAL). As soon as CS is high, the device is no longer
in the Standby mode.
An instruction following a Start condition will only be
executed if the required amount of opcode, address
and data bits for any particular instruction are clocked
in.
After execution of an instruction (i.e., clock in or out of
the last required address or data bit) CLK and DI
become don't care bits until a new Start condition is
detected.
2.2
DI/DO
It is possible to connect the Data In and Data Out pins
together. However, with this configuration it is possible
for a bus conflict to occur during the dummy zero
that precedes the read operation, if A0 is a logic high
level. Under such a condition the voltage level seen at
Data Out is undefined and will depend upon the relative
impedances of Data Out and the signal source driving
A0. The higher the current sourcing capability of A0,
the higher the voltage at the Data Out pin.
2.3
Erase/Write Enable and Disable
(EWEN, EWDS)
The 93C76/86 powers up in the Erase/Write Disable
(EWDS) state. All programming modes must be
preceded by an Erase/Write Enable (EWEN) instruction.
Once the EWEN instruction is executed, programming
remains enabled until an EWDS instruction is executed
or V
CC
is removed from the device. To protect against
accidental data disturb, the EWDS instruction can be
used to disable all erase/write functions and should
follow all programming operations. Execution of a READ
instruction is independent of both the EWEN and EWDS
instructions.
2.4
Data Protection
During power-up, all programming modes of operation
are inhibited until V
CC
has reached a level greater than
1.4V. During power-down, the source data protection
circuitry acts to inhibit all programming modes when
V
CC
has fallen below 1.4V.
The EWEN and EWDS commands give additional
protection against accidentally programming during
normal operation.
After power-up, the device is automatically in the
EWDS mode. Therefore, an EWEN instruction must be
performed before any ERASE or WRITE instruction can
be executed.

93C76/86
DS21132F-page 6
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
3.0
DEVICE OPERATION
3.1
Read
The READ instruction outputs the serial data of the
addressed memory location on the DO pin. A dummy
zero bit precedes the 16-bit (x16 organization) or 8-bit
(x8 organization) output string. The output data bits will
toggle on the rising edge of the CLK and are stable
after the specified time delay (T
PD
). Sequential read is
possible when CS is held high and clock transitions
continue. The memory address pointer will automati-
cally increment and output data sequentially.
3.2
Erase
The ERASE instruction forces all data bits of the
specified address to the logical 1 state. The self-timed
programming cycle is initiated on the rising edge of
CLK as the last address bit (A0) is clocked in. At this
point, the CLK, CS and DI inputs become dont cares.
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
device if the CS is high. The Ready/Busy status will be
displayed on the DO pin until the next Start bit is
received as long as CS is high. Bringing the CS low will
place the device in Standby mode and cause the DO
pin to enter the high-impedance state. DO at logical 0
indicates that programming is still in progress. DO at
logical 1 indicates that the register at the specified
address has been erased and the device is ready for
another instruction.
The erase cycle takes 3 ms per word (typical).
3.3
Write
The WRITE instruction is followed by 16 bits (or by 8
bits) of data to be written into the specified address.
The self-timed programming cycle is initiated on the
rising edge of CLK as the last data bit (D0) is clocked
in. At this point, the CLK, CS and DI inputs become
dont cares.
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
device if the CS is high. The Ready/Busy status will be
displayed on the DO pin until the next Start bit is
received as long as CS is high. Bringing the CS low will
place the device in Standby mode and cause the DO
pin to enter the high-impedance state. DO at logical 0
indicates that programming is still in progress. DO at
logical 1 indicates that the register at the specified
address has been written and the device is ready for
another instruction.
The write cycle takes 3 ms per word (typical).
3.4
Erase All (ERAL)
The ERAL instruction will erase the entire memory array
to the logical 1 state. The ERAL cycle is identical to
the erase cycle except for the different opcode. The
ERAL cycle is completely self-timed and commences
on the rising edge of the last address bit (A0). Note that
the Least Significant 8 or 9 address bits are "dont care"
bits, depending on selection of x16 or x8 mode. Clock-
ing of the CLK pin is not necessary after the device has
entered the self clocking mode. The ERAL instruction is
ensured at Vcc = +4.5V to +5.5V.
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
device if the CS is high. The Ready/Busy status will be
displayed on the DO pin until the next Start bit is
received as long as CS is high. Bringing the CS low will
place the device in Standby mode and cause the DO
pin to enter the high-impedance state. DO at logical 0
indicates that programming is still in progress. DO at
logical 1 indicates that the entire device has been
erased and is ready for another instruction.
The ERAL cycle takes 15 ms maximum (8 ms typical).
3.5
Write All (WRAL)
The WRAL instruction will write the entire memory array
with the data specified in the command. The WRAL
cycle is completely self-timed and commences on the
rising edge of the last address bit (A0). Note that the
Least Significant 8 or 9 address bits are dont cares,
depending on selection of x16 or x8 mode. Clocking of
the CLK pin is not necessary after the device has
entered the self clocking mode. The WRAL command
does include an automatic ERAL cycle for the device.
Therefore, the WRAL instruction does not require an
ERAL
instruction but the chip must be in the EWEN
status. The WRAL instruction is ensured at Vcc = +4.5V
to +5.5V.
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
device if the CS is high. The Ready/Busy status will be
displayed on the DO pin until the next Start bit is
received as long as CS is high. Bringing the CS low will
place the device in Standby mode and cause the DO
pin to enter the high-impedance state. DO at logical 0
indicates that programming is still in progress. DO at
logical 1 indicates that the entire device has been
written and is ready for another instruction.
The WRAL cycle takes 30 ms maximum (16 ms
typical).
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 7
93C76/86
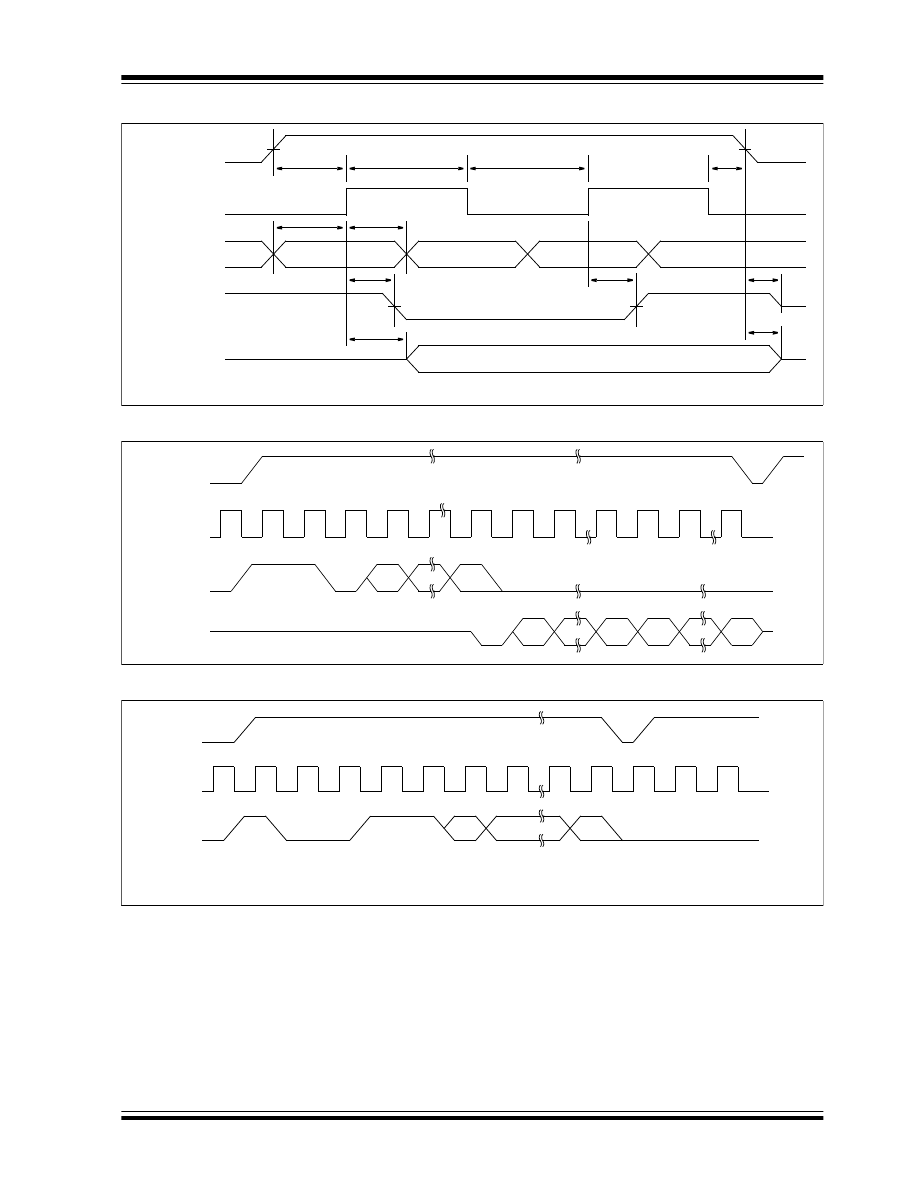
FIGURE 3-1:
SYNCHRONOUS DATA TIMING
FIGURE 3-2:
READ
FIGURE 3-3:
EWEN
The memory automatically cycles to the next register.
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
IL
T
SV
T
DIS
T
PD
T
DIH
T
CSS
T
CKH
T
CKL
T
PD
T
CSH
T
CZ
T
CZ
CS
CLK
DI
DO
DO
(Program)
(Read)
Status Valid
1
1
0
A
N
A
0
D
N
D
N
D
0
D
0
...
...
...
High-impedance
T
CSL
CS
CLK
DI
DO
0
EWEN
CS
CLK
DI
1
1
1
0
0
T
CSL
x
x
...
ORG = V
CC
, 8 XS
ORG = V
SS
, 9 XS
93C76/86
DS21132F-page 8
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
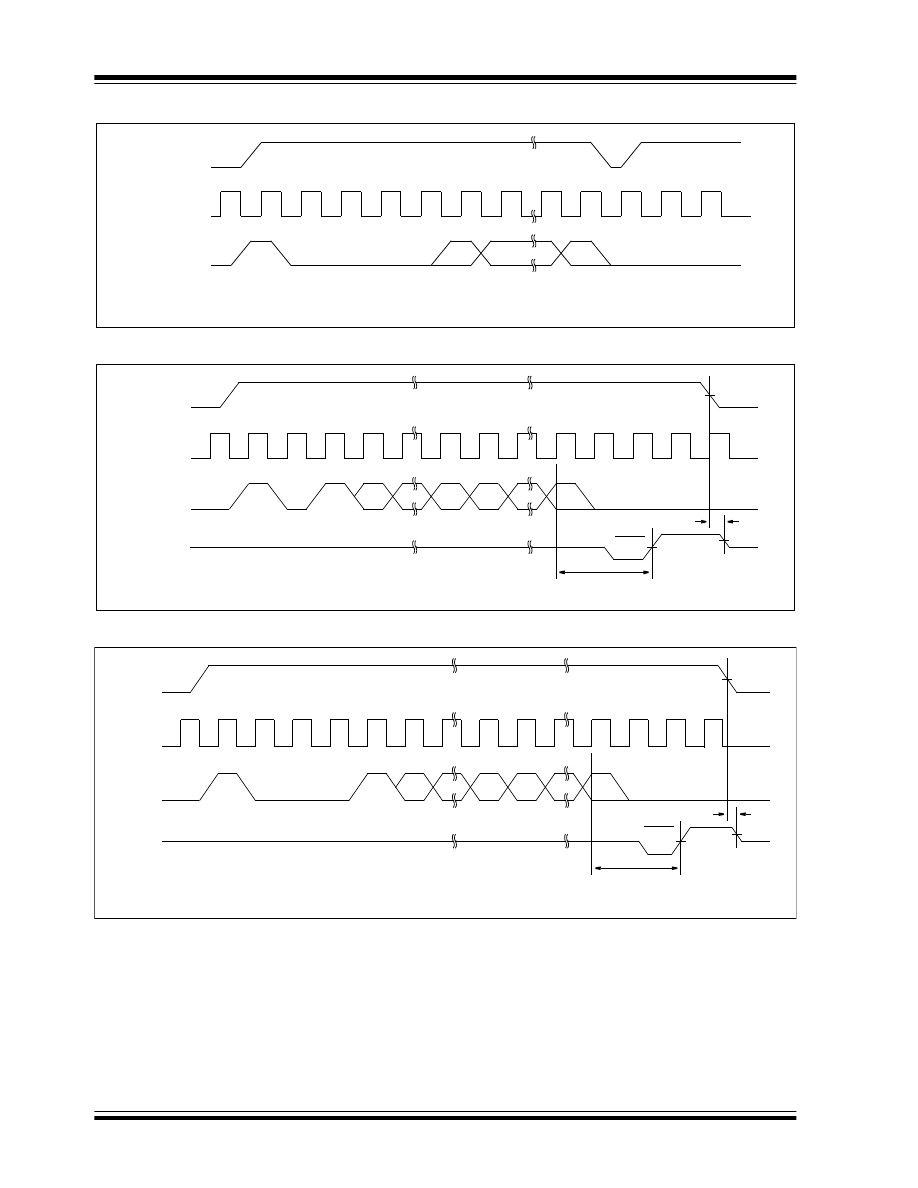
FIGURE 3-4:
EWDS
FIGURE 3-5:
WRITE
FIGURE 3-6:
WRAL
1
0
0
0
0
x
x
...
CS
CLK
DI
T
CSL
ORG = V
CC
, 8 Xs
ORG = V
SS
, 9 XS
1
0
1
A
N
A
0
...
D
N
...
D
0
T
WC
Ready
Busy
High-impedance
CS
CLK
DI
DO
Standby
T
CZ
Ensure at Vcc = +4.5V to +5.5V.
1
0
0
0
1
x
...
x
D
N
...
D
0
Busy
Ready
High-impedance
Standby
CS
CLK
DI
DO
ORG = V
CC
, 8 Xs
ORG = V
SS
, 9 Xs
T
WL
T
CZ
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 9
93C76/86
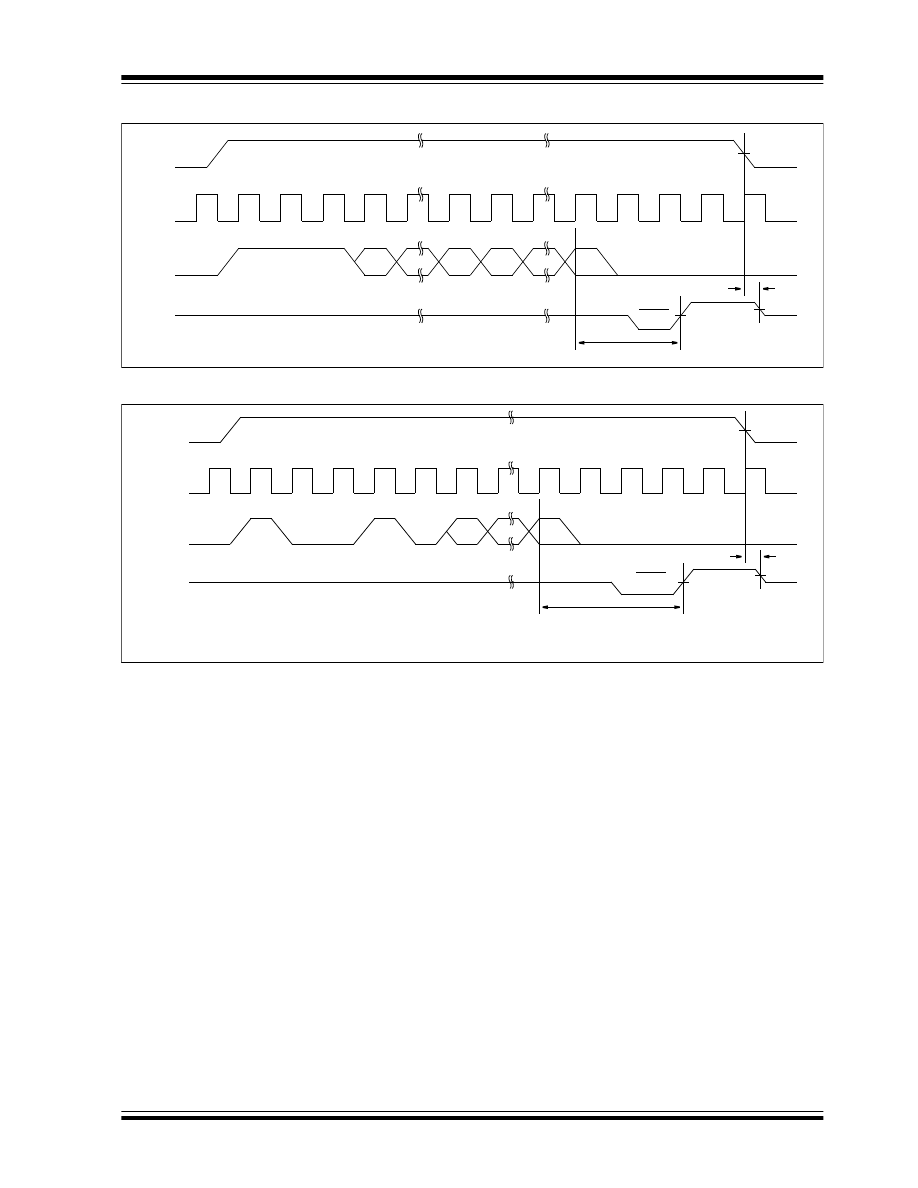
FIGURE 3-7:
ERASE
FIGURE 3-8:
ERAL
1
1
1
A
N
...
A
0
T
CZ
High-impedance
CS
CLK
DI
DO
Standby
Ready
Busy
T
WC
...
Ensure at V
CC
= +4.5V to +5.5V.
ORG = V
CC
, 8 Xs
ORG = V
SS
, 9 Xs
1
0
0
1
0
x
x
...
CS
CLK
DI
DO
T
EC
T
CZ
High-impedance
Busy
Ready
Standby
93C76/86
DS21132F-page 10
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
4.0
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
TABLE 4-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
4.1
Chip Select (CS)
A high level selects the device. A low level deselects
the device and forces it into Standby mode. However, a
programming cycle which is already initiated will be
completed, regardless of the CS input signal. If CS is
brought low during a program cycle, the device will go
into Standby mode as soon as the programming cycle
is completed.
CS must be low for 250 ns minimum (T
CSL
) between
consecutive instructions. If CS is low, the internal
control logic is held in a RESET status.
4.2
Serial Clock (CLK)
The Serial Clock is used to synchronize the communi-
cation between a master device and the 93C76/86.
Opcode, address and data bits are clocked in on the
positive edge of CLK. Data bits are also clocked out on
the positive edge of CLK.
CLK can be stopped anywhere in the transmission
sequence (at high or low level) and can be continued
anytime with respect to clock high time (T
CKH
) and
clock low time (T
CKL
). This gives the controlling master
freedom in preparing opcode, address and data.
CLK is a don't care if CS is low (device deselected). If
CS is high, but Start condition has not been detected,
any number of clock cycles can be received by the
device without changing its status (i.e., waiting for Start
condition).
CLK cycles are not required during the self-timed write
(i.e., auto erase/write) cycle.
After detection of a Start condition the specified number
of clock cycles (respectively low-to-high transitions of
CLK) must be provided. These clock cycles are
required to clock in all opcode, address, and data bits
before an instruction is executed (seethrougr more details). CLK and DI then
become don't care inputs waiting for a new Start
condition to be detected.
4.3
Data In (DI)
Data In is used to clock in a Start bit, opcode, address
and data synchronously with the CLK input.
4.4
Data Out (DO)
Data Out is used in the Read mode to output data
synchronously with the CLK input (T
PD
after the
positive edge of CLK).
This pin also provides Ready/Busy status information
during erase and write cycles. Ready/Busy status
information is available when CS is high. It will be
displayed until the next Start bit occurs as long as CS
stays high.
4.5
Organization (ORG)
When ORG is connected to V
CC
, the x16 memory
organization is selected. When ORG is tied to V
SS
, the
x8 memory organization is selected. There is an
internal pull-up resistor on the ORG pin that will select
x16 organization when left unconnected.
4.6
Program Enable (PE)
This pin allows the user to enable or disable the ability
to write data to the memory array. If the PE pin is
floated or tied to V
CC
, the device can be programmed.
If the PE pin is tied to V
SS
, programming will be
inhibited. There is an internal pull-up on this device that
enables programming if this pin is left floating.
Name
Function
CS
Chip Select
CLK
Serial Data Clock
DI
Serial Data Input
DO
Serial Data Output
V
SS
Ground
ORG
Memory Configuration
PE
Program Enable
V
CC
Power Supply
Note:
CS must go low between consecutive
instructions, except when performing a
sequential read (Refer to for more detail on sequential
reads).
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 11
93C76/86
5.0
PACKAGING INFORMATION
5.1
Package Marking Information
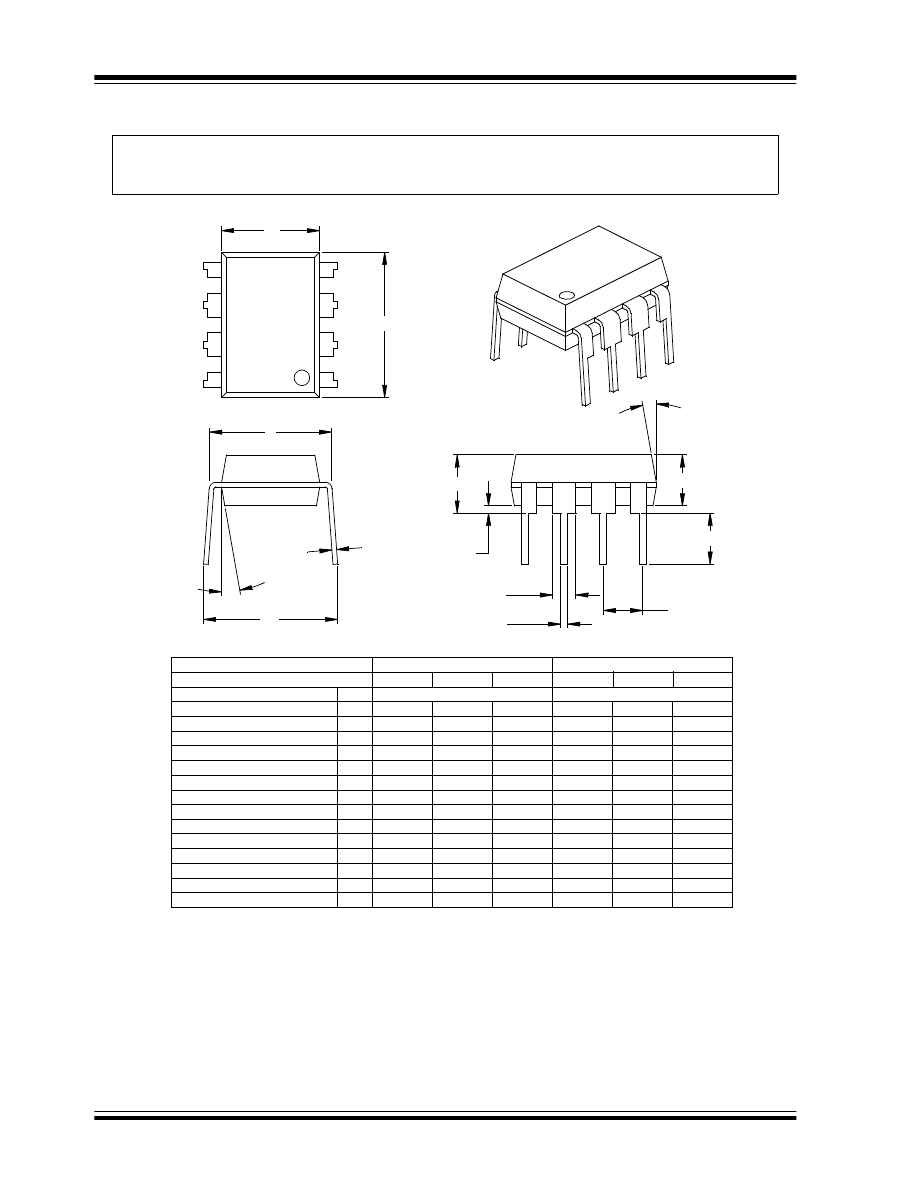
XXXXXNNN
8-Lead PDIP
XXXXXXXX
YYWW
017
Example
93C76
0410
8-Lead SOIC (.150)
XXXXXXXX
XXXXYYWW
NNN
Example
93C86
/SN0410
017
Legend: XX...X
Customer-specific information
Y
Year code (last digit of calendar year)
YY
Year code (last 2 digits of calendar year)
WW
Week code (week of January 1 is week 01)
NNN
Alphanumeric traceability code
Pb-free JEDEC designator for Matte Tin (Sn)
*
This package is Pb-free. The Pb-free JEDEC designator ( )
can be found on the outer packaging for this package.
Note:
In the event the full Microchip part number cannot be marked on one line, it will
be carried over to the next line, thus limiting the number of available
characters for customer-specific information.
3
e
3
e
93C76/86
DS21132F-page 12
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
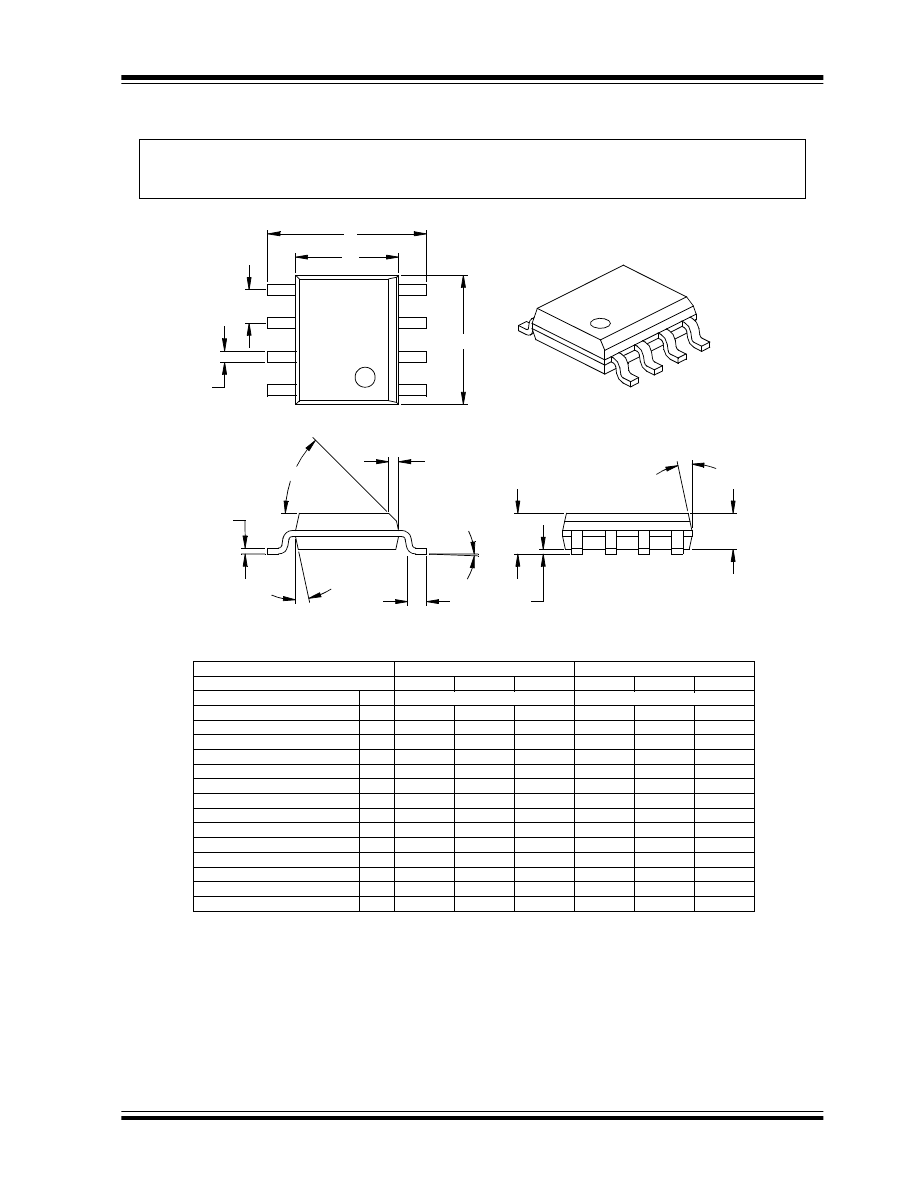
8-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) - 300 mil Body (PDIP)
B1
B
A1
A
L
A2
p
ï¡
E
eB
ï¢
c
E1
n
D
1
2
Units
INCHES*
MILLIMETERS
Dimension Limits
MIN
NOM
MAX
MIN
NOM
MAX
Number of Pins
n
8
8
Pitch
p
.100
2.54
Top to Seating Plane
A
.140
.155
.170
3.56
3.94
4.32
Molded Package Thickness
A2
.115
.130
.145
2.92
3.30
3.68
Base to Seating Plane
A1
.015
0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width
E
.300
.313
.325
7.62
7.94
8.26
Molded Package Width
E1
.240
.250
.260
6.10
6.35
6.60
Overall Length
D
.360
.373
.385
9.14
9.46
9.78
Tip to Seating Plane
L
.125
.130
.135
3.18
3.30
3.43
Lead Thickness
c
.008
.012
.015
0.20
0.29
0.38
Upper Lead Width
B1
.045
.058
.070
1.14
1.46
1.78
Lower Lead Width
B
.014
.018
.022
0.36
0.46
0.56
Overall Row Spacing
§
eB
.310
.370
.430
7.87
9.40
10.92
Mold Draft Angle Top
ï¡
5
10
15
5
10
15
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
ï¢
5
10
15
5
10
15
* Controlling Parameter
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-018
.010 (0.254mm) per side.
§ Significant Characteristic
Note:
For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located
at http://www.microchip.com/packaging
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 13
93C76/86
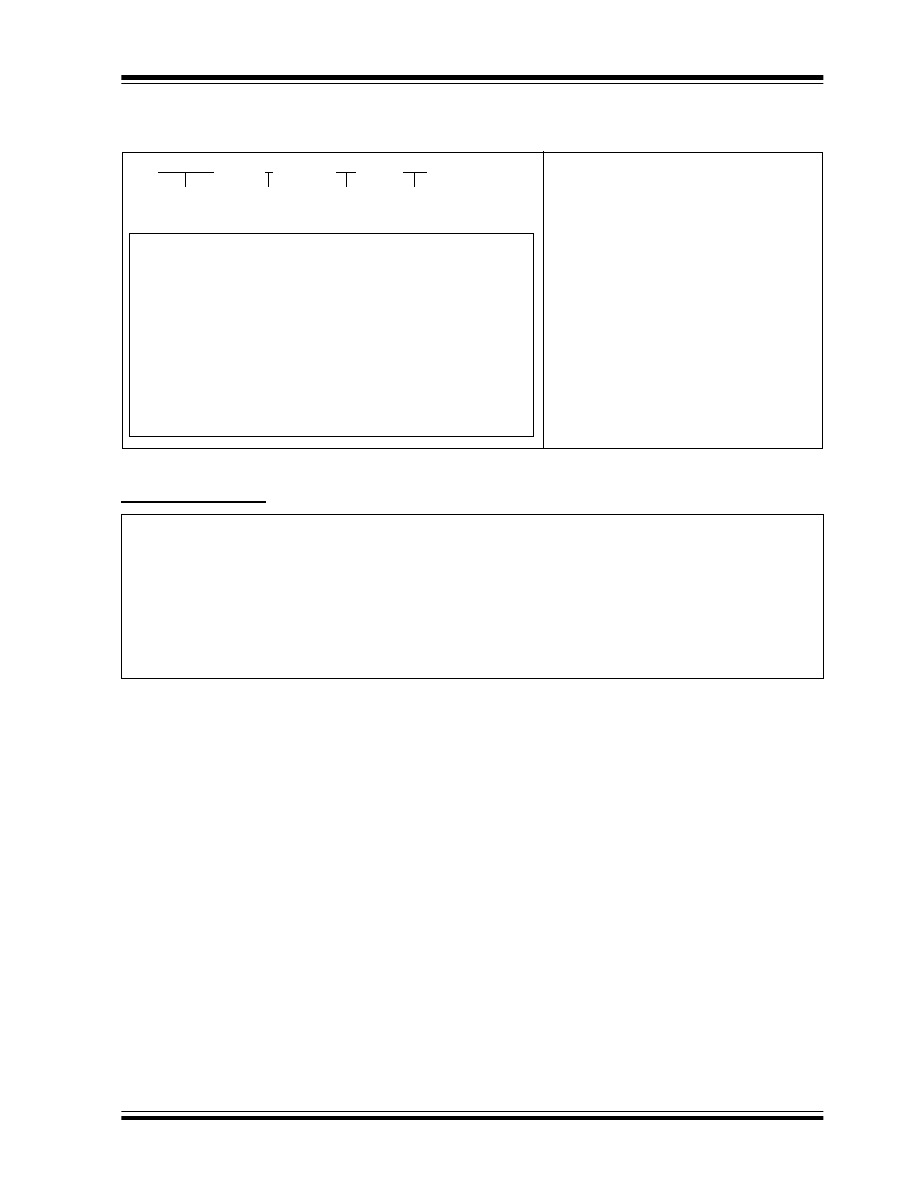
8-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SN) - Narrow, 150 mil Body (SOIC)
Foot Angle
ï¦
0
4
8
0
4
8
15
12
0
15
12
0
ï¢
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
15
12
0
15
12
0
ï¡
Mold Draft Angle Top
0.51
0.42
0.33
.020
.017
.013
B
Lead Width
0.25
0.23
0.20
.010
.009
.008
c
Lead Thickness
0.76
0.62
0.48
.030
.025
.019
L
Foot Length
0.51
0.38
0.25
.020
.015
.010
h
Chamfer Distance
5.00
4.90
4.80
.197
.193
.189
D
Overall Length
3.99
3.91
3.71
.157
.154
.146
E1
Molded Package Width
6.20
6.02
5.79
.244
.237
.228
E
Overall Width
0.25
0.18
0.10
.010
.007
.004
A1
Standoff
§
1.55
1.42
1.32
.061
.056
.052
A2
Molded Package Thickness
1.75
1.55
1.35
.069
.061
.053
A
Overall Height
1.27
.050
p
Pitch
8
8
n
Number of Pins
MAX
NOM
MIN
MAX
NOM
MIN
Dimension Limits
MILLIMETERS
INCHES*
Units
2
1
D
n
p
B
E
E1
h
L
ï¢
c
45
ï°
ï¦
A2
ï¡
A
A1
* Controlling Parameter
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010 (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-057
§ Significant Characteristic
Note:
For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located
at http://www.microchip.com/packaging

93C76/86
DS21132F-page 14
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
APPENDIX A:
REVISION HISTORY
Revision E
Added note to page 1 header (Not recommended for
new designs).
Added Section 5.0: Package Marking Information.
Added On-line Support page.
Updated document format.
Revision F
Added a note to each package outline drawing.

ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 15
93C76/86
THE MICROCHIP WEB SITE
.microchip.com
. This web site is used as a means
to make files and information easily available to
customers. Accessible by using your favorite Internet
browser, the web site contains the following
information:
Product Support - Data sheets and errata,
application notes and sample programs, design
resources, users guides and hardware support
documents, latest software releases and archived
software
General Technical Support - Frequently Asked
Questions (FAQ), technical support requests,
online discussion groups, Microchip consultant
program member listing
Business of Microchip - Product selector and
ordering guides, latest Microchip press releases,
listing of seminars and events, listings of
Microchip sales offices, distributors and factory
representatives
CUSTOMER CHANGE NOTIFICATION
SERVICE
Microchips customer notification service helps keep
customers current on Microchip products. Subscribers
will receive e-mail notification whenever there are
changes, updates, revisions or errata related to a
specified product family or development tool of interest.
.microchip.com
. Under Support, click on
Customer Change Notification and follow the
registration instructions.
CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance
through several channels:
Distributor or Representative
Local Sales Office
Field Application Engineer (FAE)
Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor,
representative or field application engineer (FAE) for
support. Local sales offices are also available to help
customers. A listing of sales offices and locations is
included in the back of this document.
/microchip.com/support

93C76/86
DS21132F-page 16
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
READER RESPONSE
It is our intention to provide you with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
product. If you wish to provide your comments on organization, clarity, subject matter, and ways in which our
documentation can better serve you, please FAX your comments to the Technical Publications Manager at
(480) 792-4150.
Please list the following information, and use this outline to provide us with your comments about this document.
TO:
Technical Publications Manager
RE:
Reader Response
Total Pages Sent ________
From: Name
Company
Address
City / State / ZIP / Country
Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________
Application (optional):
Would you like a reply? Y N
Device: Literature
Number:
Questions:
FAX: (______) _________ - _________
DS21132F
93C76/86
1.
What are the best features of this document?
2.
How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs?
3.
Do you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why?
4.
What additions to the document do you think would enhance the structure and subject?
5.
What deletions from the document could be made without affecting the overall usefulness?
6.
Is there any incorrect or misleading information (what and where)?
7.
How would you improve this document?
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 17
93C76/86
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office
.
Sales and Support
PART NO.
X
/XX
XXX
Pattern
Package
Temperature
Range
Device
Device
93C76/86: Microwire Serial EEPROM
93C76T/86T: Microwire Serial EEPROM (Tape and Reel)
Temperature Range
Blank
=
0
ï°C to +70ï°C
I
= -40
ï°C to +85ï°C
E
= -40
ï°C to +125ï°C
Package
P
=
Plastic DIP (300 mil Body), 8-lead
SN
=
Plastic SOIC (150 mil Body), 8-lead
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and
recommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of the following:
1.
Your local Microchip sales office
2.
The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.

93C76/86
DS21132F-page 18
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
NOTES:

ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21132F-page 19
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION,
QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability
arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at
the buyers risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and
hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims,
suits, or expenses resulting from such use. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip
intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, dsPIC,
FlashFlex, K
EE
L
OQ
, K
EE
L
OQ
logo, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro,
PICSTART, PIC
32
logo, rfPIC, SST, SST Logo, SuperFlash
and UNI/O are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, Hampshire, HI-TECH C, Linear Active Thermistor,
MTP, SEEVAL and The Embedded Control Solutions
Company are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Silicon Storage Technology is a registered trademark of
Microchip Technology Inc. in other countries.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, BodyCom,
chipKIT, chipKIT logo, CodeGuard, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, dsSPEAK, ECAN,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, HI-TIDE, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPF, MPLAB
Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, mTouch, Omniscient Code
Generation, PICC, PICC-18, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PICkit,
PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, SQI, Serial Quad I/O,
Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock, ZENA
and Z-Scale are trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
GestIC and ULPP are registered trademarks of Microchip
Technology Germany II GmbH & Co. & KG, a subsidiary of
Microchip Technology Inc., in other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 1996-2012, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in
the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
ISBN: 9781620767412
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchips Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as unbreakable.
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchips code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2009 certification for its worldwide
headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and
Tempe, Arizona; Gresham, Oregon and design centers in California
and India. The Companys quality system processes and procedures
are for its PIC
®
MCUs and dsPIC
®
DSCs, K
EE
L
OQ
®
code hopping
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchips quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CERTIFIED BY DNV
==
ISO/TS 16949
==

DS21132F-page 20
ï£ 1996-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
Web Address:
.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Cleveland
Independence, OH
Tel: 216-447-0464
Fax: 216-447-0643
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Farmington Hills, MI
Tel: 248-538-2250
Fax: 248-538-2260
Indianapolis
Noblesville, IN
Tel: 317-773-8323
Fax: 317-773-5453
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Santa Clara
Santa Clara, CA
Tel: 408-961-6444
Fax: 408-961-6445
Toronto
Mississauga, Ontario,
Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Asia Pacific Office
Suites 3707-14, 37th Floor
Tower 6, The Gateway
Harbour City, Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8569-7000
Fax: 86-10-8528-2104
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
Fax: 86-28-8665-7889
China - Chongqing
Tel: 86-23-8980-9588
Fax: 86-23-8980-9500
China - Hangzhou
Tel: 86-571-2819-3187
Fax: 86-571-2819-3189
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Nanjing
Tel: 86-25-8473-2460
Fax: 86-25-8473-2470
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
Fax: 86-532-8502-7205
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-5407-5533
Fax: 86-21-5407-5066
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
Fax: 86-24-2334-2393
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8203-2660
Fax: 86-755-8203-1760
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
Fax: 86-27-5980-5118
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7252
Fax: 86-29-8833-7256
China - Xiamen
Tel: 86-592-2388138
Fax: 86-592-2388130
China - Zhuhai
Tel: 86-756-3210040
Fax: 86-756-3210049
ASIA/PACIFIC
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-3090-4444
Fax: 91-80-3090-4123
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
Fax: 91-11-4160-8632
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-2566-1512
Fax: 91-20-2566-1513
Japan - Osaka
Tel: 81-66-152-7160
Fax: 81-66-152-9310
Japan - Yokohama
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166
Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea - Daegu
Tel: 82-53-744-4301
Fax: 82-53-744-4302
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 60-3-6201-9857
Fax: 60-3-6201-9859
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-227-8870
Fax: 60-4-227-4068
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Fax: 63-2-634-9069
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-5778-366
Fax: 886-3-5770-955
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-213-7828
Fax: 886-7-330-9305
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2508-8600
Fax: 886-2-2508-0102
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Fax: 66-2-694-1350
EUROPE
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
Worldwide Sales and Service
10/26/12
Document Outline

